The Reality Of Bringing Factory Jobs Back To The US: A Critical Analysis

Table of Contents
The promise of bringing factory jobs back to the US is a potent political and economic talking point. However, the reality is far more nuanced than simple slogans suggest. This critical analysis examines the multifaceted challenges and opportunities surrounding reshoring, exploring the key factors that determine its success or failure. We'll delve into the economic realities, technological advancements, and policy implications involved in this complex issue.
The Economic Landscape of Reshoring
The economic viability of reshoring is a significant hurdle. Simply put, manufacturing in the US often comes with substantially higher costs than in many other countries.
High Labor Costs in the US
US wages and benefits for manufacturing workers significantly exceed those in competing nations. This difference dramatically impacts a company's competitiveness on the global market.
- US Average Manufacturing Wage: While precise figures fluctuate, US average manufacturing wages consistently surpass those in countries like China, Mexico, and Vietnam by a considerable margin.
- Benefits Costs: Employee benefits in the US, including healthcare and retirement plans, add substantial costs compared to many other manufacturing hubs. These costs are often significantly lower or non-existent in countries with less robust social safety nets.
- Unionization Impact: Unionized workplaces in the US often command higher wages and benefits, further increasing labor costs compared to non-unionized factories overseas.
Infrastructure and Transportation Costs
The US faces challenges with aging infrastructure, impacting transportation efficiency and adding costs to the manufacturing process.
- Infrastructure Upgrading Costs: Modernizing roads, ports, and railways requires substantial investment, which ultimately adds to the overall cost of manufacturing in the US.
- Transportation Network Efficiency: Compared to countries with more modern and integrated transportation networks, the US often faces higher transportation costs and longer delivery times. This inefficiency can hinder competitiveness.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental cost of transportation should also be considered. The carbon footprint associated with moving goods across the US may be higher than in countries with more geographically concentrated manufacturing hubs.
Automation and Technological Advancements
Automation and robotics are transforming the manufacturing landscape, impacting the demand for traditional factory jobs. While this technology offers opportunities, it also presents challenges.
- AI and Automation Cost Reduction: The implementation of AI and automation technologies can dramatically reduce labor costs in the long run, making manufacturing more competitive.
- Job Displacement and Reskilling: The automation of manufacturing processes inevitably leads to job displacement for some workers. However, it also creates a need for new skilled labor in areas such as automation maintenance and programming. Investment in reskilling initiatives is crucial.
- Higher-Skilled Jobs: The future of manufacturing in the US will likely involve a shift toward higher-skilled jobs focused on technology, design, and management of automated systems.
Political and Policy Implications of Reshoring
Government policies and trade agreements play a crucial role in the success or failure of reshoring initiatives.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Various government programs offer tax breaks and grants to encourage companies to bring manufacturing back to the US. The effectiveness of these incentives is a subject of ongoing debate.
- Tax Breaks and Grants: Examples include tax credits for investments in new equipment, grants for facility construction, and other financial incentives designed to offset the higher costs of domestic manufacturing.
- Incentive Effectiveness: The effectiveness of these incentives varies greatly depending on their design and implementation. Some argue they're insufficient to overcome the cost disadvantages of manufacturing in the US.
- Potential Drawbacks: Some critics worry that excessive subsidies could lead to unfair competition or misallocation of resources.
Trade Agreements and Tariffs
Trade policies, tariffs, and trade wars significantly affect the cost and feasibility of reshoring.
- Tariff Impact on Import Costs: Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, potentially making domestically produced goods more competitive. However, tariffs can also lead to retaliatory measures from other countries.
- Global Supply Chain Effects: Trade agreements shape the global supply chain, impacting the accessibility and cost of raw materials and components.
- Protectionism's Unintended Consequences: Protectionist trade policies can have unintended negative consequences, including higher consumer prices and disruptions to global trade relationships.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
The US regulatory environment impacts the attractiveness of the country for manufacturers.
- US vs. Other Countries: The US regulatory landscape, particularly regarding environmental and labor standards, is often stricter than in other manufacturing hubs. This increases compliance costs for businesses.
- Environmental Regulations: Stringent environmental regulations, while beneficial for the environment, can increase manufacturing costs compared to countries with less stringent standards.
- Labor Regulations: Labor regulations, such as minimum wage laws and workplace safety standards, also impact the cost of manufacturing in the US.
The Future of Manufacturing in the US
The future of US manufacturing likely involves a shift towards specialized sectors and a focus on innovation.
The Rise of "Nearshoring" and Regionalization
"Nearshoring," relocating manufacturing to nearby countries like Mexico and Canada, is gaining popularity.
- Nearshoring Benefits: Nearshoring offers advantages, including reduced transportation costs and simpler logistics. It provides a balance between cost savings and proximity to the US market.
- Nearshoring Limitations: However, nearshoring still presents challenges. Labor costs in countries like Mexico are increasing, and the benefits are not as substantial as offshoring to countries like China.
Focus on High-Value Manufacturing and Innovation
The US is well-positioned to excel in high-value manufacturing sectors requiring advanced technology and skilled labor.
- Opportunities in Specialized Sectors: The US has a strong competitive advantage in sectors like advanced materials, biotechnology, and aerospace, which require high levels of research and development.
- Investing in R&D: Investment in research and development is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in these high-value manufacturing sectors.
The Need for Workforce Development and Reskilling
Investing in education and training is paramount to preparing the workforce for the jobs of the future.
- Skilled Labor Demand: Advanced manufacturing requires a skilled workforce proficient in areas such as automation, robotics, and data analysis.
- Vocational Training and Apprenticeships: Strengthening vocational training programs and apprenticeships is vital for providing the necessary skills.
- Role of Education Institutions: Community colleges and universities play a key role in providing workforce development programs and reskilling opportunities.
Conclusion
Bringing factory jobs back to the US is a multifaceted challenge. While the desire for reshoring is strong, success depends on a strategic approach that considers economic, political, and technological factors. A balanced approach combining government support with private sector investment is crucial for a revitalized US manufacturing sector. Understanding the realities of bringing factory jobs back to the US is critical for informed policymaking and economic planning. Let's continue this crucial conversation about the future of American manufacturing and explore effective strategies for reshoring and nearshoring.

Featured Posts
-
 Ferraris Response To Leclerc Speculation Before Imola
May 20, 2025
Ferraris Response To Leclerc Speculation Before Imola
May 20, 2025 -
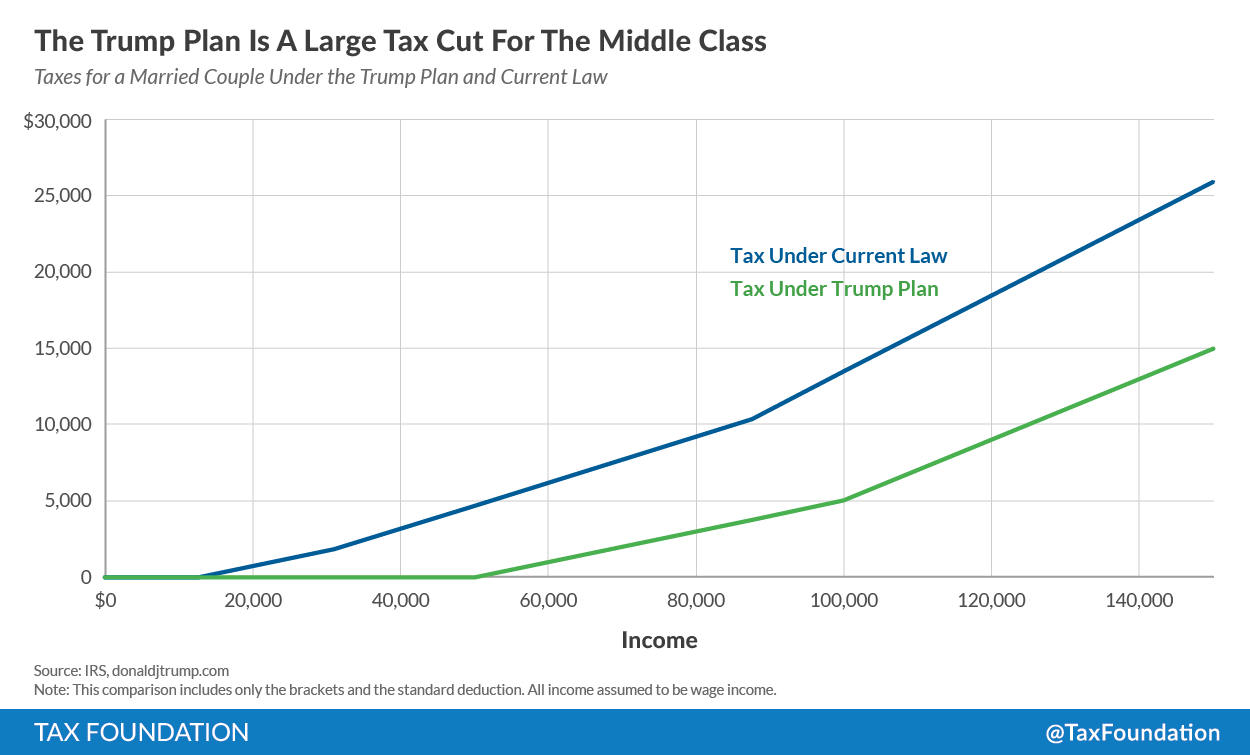 The Stark Math On The Gop Tax Plan Deficit Impact Analysis
May 20, 2025
The Stark Math On The Gop Tax Plan Deficit Impact Analysis
May 20, 2025 -
 Beyond Edward Cullen Exploring The Love Lives Of Twilights Cast
May 20, 2025
Beyond Edward Cullen Exploring The Love Lives Of Twilights Cast
May 20, 2025 -
 15 Avril Mise En Place De Restrictions De Circulation Pour Les 2 Et 3 Roues Sur Le Boulevard Fhb
May 20, 2025
15 Avril Mise En Place De Restrictions De Circulation Pour Les 2 Et 3 Roues Sur Le Boulevard Fhb
May 20, 2025 -
 Tadi Shmit E Tri Godine Podstitsao Sukobe A Sada Pere Ruke
May 20, 2025
Tadi Shmit E Tri Godine Podstitsao Sukobe A Sada Pere Ruke
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Aryna Sabalenkas Winning Start At The Madrid Open
May 20, 2025
Aryna Sabalenkas Winning Start At The Madrid Open
May 20, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues April 26 2025
May 20, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues April 26 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers March 26 2025
May 20, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers March 26 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Hints And Solutions April 26 2025
May 20, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Hints And Solutions April 26 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Ginger Zee Slams Critic Over Aging Comments
May 20, 2025
Ginger Zee Slams Critic Over Aging Comments
May 20, 2025
