The US Increases Tariffs On Solar Imports From Southeast Asia: Economic Effects
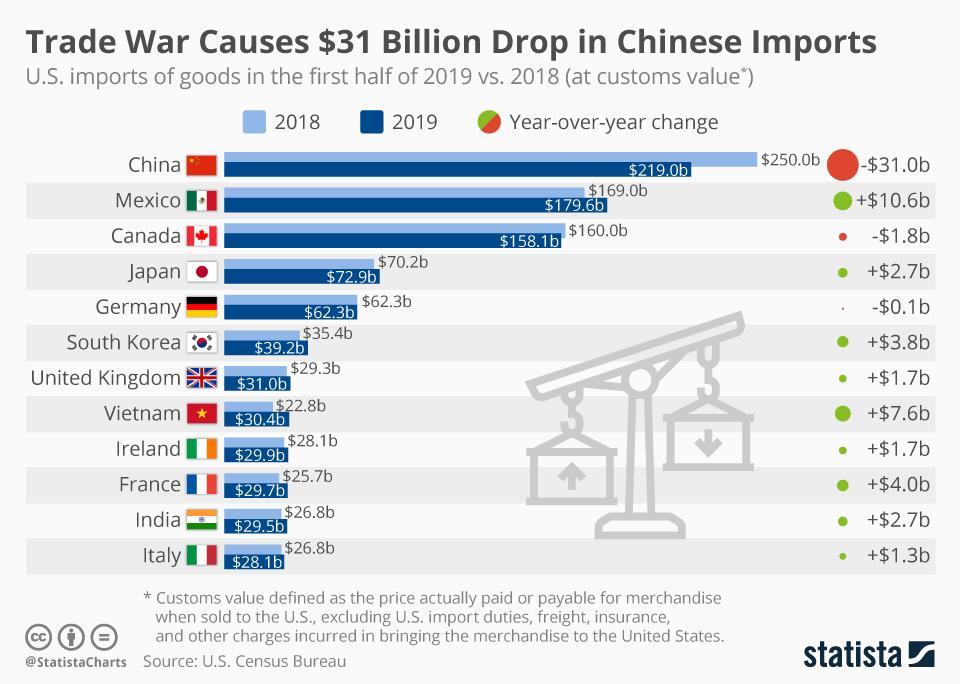
Table of Contents
Impact on US Solar Energy Sector
The immediate effect of the increased US solar tariffs is felt most acutely within the domestic solar energy sector.
Increased Solar Panel Prices
- Higher Costs for Consumers: The tariffs directly translate to higher prices for solar panels in the US. This increased cost of solar panel installation can significantly reduce consumer demand, potentially slowing the growth of the solar energy market. Many homeowners and businesses may postpone or cancel projects due to increased upfront costs.
- Slowdown in US Solar Industry Growth: Reduced consumer demand inevitably impacts the overall growth of the US solar energy industry. This could mean fewer installations, less investment in new solar projects, and a potential slowdown in job creation within the sector.
- Impact on Solar Energy Jobs: While the tariffs aim to boost domestic solar manufacturing, the initial impact may be a decrease in jobs within the installation and maintenance sectors due to reduced demand. However, increased domestic manufacturing could create new jobs, although the net effect on employment remains uncertain and depends on the speed and scale of domestic production increases. It's a complex issue with both positive and negative potential employment consequences.
- Keywords: US solar prices, solar panel costs, consumer demand, solar energy jobs, solar industry growth.
Effect on Domestic Solar Manufacturing
The intended beneficiary of these tariffs is the US domestic solar manufacturing sector.
- Increased Competitiveness: Higher import costs level the playing field, making US-produced solar panels more competitive against cheaper imports from Southeast Asia. This could attract investment and encourage expansion of domestic manufacturing facilities.
- Potential for Job Creation: Increased domestic production could lead to job creation in US solar panel factories and related industries. However, the scale of job creation will depend on the capacity of US manufacturers to quickly ramp up production to meet the demand.
- Challenges for US Manufacturers: Meeting the increased demand poses significant challenges for US manufacturers. They need to invest heavily in infrastructure, skilled labor, and supply chains, to ensure they can effectively meet the increased demand without significant delays. This is a crucial factor in determining whether the intended benefits of the tariffs will actually materialize.
- Keywords: domestic solar manufacturing, US solar manufacturers, job creation, solar panel production.
Economic Repercussions for Southeast Asian Countries
The increased US tariffs have significant economic repercussions for Southeast Asian nations heavily involved in solar panel exports.
Reduced Exports and Revenue
- Loss of Export Revenue: The decreased demand from the US market leads to a substantial reduction in export revenue for Southeast Asian countries specializing in solar panel manufacturing. This could have significant negative impacts on their GDP and overall economic health.
- Job Losses in the Solar Sector: The reduced exports will inevitably lead to job losses within the Southeast Asian solar manufacturing sector, impacting the livelihoods of many workers and potentially increasing unemployment rates in the affected countries.
- Impact on Economic Growth: The combined effects of reduced export revenue and job losses negatively affect overall economic growth in these exporting nations. This can trigger wider economic instability and potentially necessitate government intervention to mitigate the effects.
- Keywords: Southeast Asia economy, solar exports, economic growth, job losses, trade deficit.
Shifting Trade Dynamics
The tariffs are likely to trigger shifts in global trade patterns within the solar industry.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Other regions, such as Europe or India, could become more prominent suppliers of solar panels to the US market, leading to a reshuffling of global supply chains.
- Impact on Existing Trade Agreements: The tariffs could strain existing trade agreements and relationships between the US and Southeast Asian nations, potentially leading to retaliatory measures and further trade disputes.
- Emergence of New Supply Chains: The increased demand from regions outside of Southeast Asia might encourage the development of new solar manufacturing hubs and supply chains, altering the global landscape of the solar industry.
- Keywords: global solar trade, trade agreements, supply chain, solar imports, global trade dynamics.
Global Implications of the Tariff Increase
The US tariff increase has far-reaching consequences for global efforts towards renewable energy transition.
Impact on Global Solar Energy Adoption
- Increased Cost of Solar Energy Worldwide: The tariffs could lead to increased prices for solar panels globally, as the reduction in US demand from Southeast Asian suppliers may lead to surplus capacity and downward pressure on prices in other markets. However, this effect is likely to be regionally variable.
- Potential Slowdown in Global Solar Energy Adoption: Higher prices can hinder the widespread adoption of solar energy in countries already struggling with energy affordability, potentially slowing down progress towards global renewable energy targets.
- Impact on Climate Change Mitigation Goals: A slower transition to renewable energy sources, caused by higher solar panel costs, could negatively impact efforts to mitigate climate change, delaying the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Keywords: renewable energy, global solar energy adoption, climate change, clean energy transition.
Geopolitical Considerations
The tariff increase has significant geopolitical implications, potentially impacting US relations with Southeast Asian countries.
- Trade Tensions and Retaliatory Measures: The tariffs could trigger trade tensions and potential retaliatory measures from Southeast Asian nations, escalating into broader trade disputes.
- Impact on US Foreign Policy: The impact of the tariffs on US relationships with Southeast Asian countries may influence future US foreign policy decisions and strategic partnerships in the region.
- Keywords: geopolitics, US foreign policy, trade tensions, international relations.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of US Solar Tariffs and Southeast Asian Trade
The increased US tariffs on solar imports from Southeast Asia have wide-ranging economic consequences. These tariffs affect the price of solar panels in the US, impacting consumer demand and the growth of the domestic solar industry. Simultaneously, Southeast Asian economies face reduced export revenue, job losses, and shifts in global trade dynamics. The global push towards renewable energy could also be hindered by increased solar panel prices. Policymakers, businesses, and consumers need to understand these complex implications. Potential solutions could include exploring alternative supply chains, fostering domestic manufacturing capacity, and promoting international cooperation to ensure a stable and sustainable global solar energy market. To stay informed about the evolving impact of US solar tariffs and their consequences on the global solar energy market and Southeast Asian economies, continue researching this critical area. Stay informed on further developments in US solar tariffs and their far-reaching effects.

Featured Posts
-
 Free Market Education Reaches Argentina Milei And The Tuttle Twins
May 30, 2025
Free Market Education Reaches Argentina Milei And The Tuttle Twins
May 30, 2025 -
 Analysis The Ripple Effect Of Trump Tariffs On Indias Solar Energy Exports To Southeast Asia
May 30, 2025
Analysis The Ripple Effect Of Trump Tariffs On Indias Solar Energy Exports To Southeast Asia
May 30, 2025 -
 The Role Of Algorithms In Radicalization Investigating Mass Shooter Cases
May 30, 2025
The Role Of Algorithms In Radicalization Investigating Mass Shooter Cases
May 30, 2025 -
 Norrie Upsets Medvedev Djokovic Advances At French Open
May 30, 2025
Norrie Upsets Medvedev Djokovic Advances At French Open
May 30, 2025 -
 Rajinikanth Honors Ilaiyaraajas London Symphony Success
May 30, 2025
Rajinikanth Honors Ilaiyaraajas London Symphony Success
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 When And Where Estevans 2024 Road Sweeping Schedule
May 31, 2025
When And Where Estevans 2024 Road Sweeping Schedule
May 31, 2025 -
 Full Street Sweeping Schedule Now Available For Estevan Residents
May 31, 2025
Full Street Sweeping Schedule Now Available For Estevan Residents
May 31, 2025 -
 Estevan Announces Complete Road Sweeping Schedule
May 31, 2025
Estevan Announces Complete Road Sweeping Schedule
May 31, 2025 -
 Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule 2024 Full Dates Released
May 31, 2025
Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule 2024 Full Dates Released
May 31, 2025 -
 Moroccan Childrens Charity Receives Support From Duncan Bannatyne
May 31, 2025
Moroccan Childrens Charity Receives Support From Duncan Bannatyne
May 31, 2025
