Trump's 30% Tariffs On China: An Extended Outlook To Late 2025
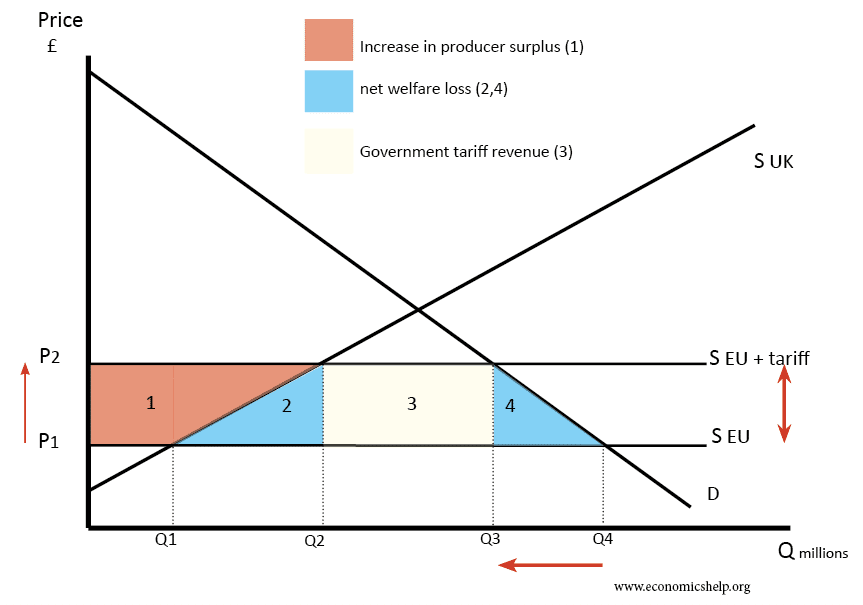
Table of Contents
Initial Impact and Immediate Economic Fallout (2018-2020)
The initial implementation of Trump's 30% tariffs on Chinese goods, beginning in 2018, sent shockwaves through the global economy. These tariffs targeted a wide range of products, from consumer electronics to agricultural goods. The immediate consequences were felt acutely by both US businesses and consumers.
- Rise in prices of imported goods: The tariffs directly increased the cost of many imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and impacting affordability. This was particularly noticeable in sectors reliant on Chinese imports, driving up inflation.
- Impact on US businesses reliant on Chinese imports: Many US businesses that relied heavily on Chinese imports faced increased production costs, reduced profit margins, and in some cases, were forced to raise their prices or even shut down operations. This highlighted the interconnectedness of global supply chains.
- Retaliatory tariffs imposed by China: China responded to the US tariffs with its own retaliatory measures, imposing tariffs on US goods. This tit-for-tat escalation further disrupted global trade flows and exacerbated the economic uncertainty.
- Shifting global supply chains: Businesses began to explore alternatives to sourcing from China, leading to a significant shift in global supply chains. This process, known as "reshoring" (returning production to the US) or "nearshoring" (moving production to nearby countries), proved to be a long and complex undertaking.
The Biden Administration and Tariff Adjustments (2021-Present)
The Biden administration inherited the complex legacy of Trump's 30% tariffs on China. While President Biden hasn't completely removed the tariffs, his approach has been more nuanced, focusing on targeted adjustments rather than a complete reversal.
- Review of the Trump-era tariffs: The Biden administration initiated a comprehensive review of the tariffs imposed by the previous administration, assessing their effectiveness and impact on various sectors.
- Partial tariff removals or adjustments: Certain tariffs have been removed or reduced, particularly on some consumer goods. However, many tariffs remain in place, particularly those impacting strategically important sectors.
- Focus on strategic sectors: The Biden administration has emphasized targeting tariffs strategically, focusing on sectors deemed crucial for national security or technological advancement.
- Ongoing trade negotiations: Trade negotiations between the US and China have continued, albeit with limited progress on significant tariff reductions. These negotiations reflect the complex and multifaceted nature of the relationship.
Long-Term Economic Effects on the US Economy
The long-term economic effects of Trump's 30% tariffs on China continue to unfold. While some argue the tariffs were necessary to protect US industries, others point to negative consequences for consumers and overall economic growth.
- Persistent inflation pressures: The tariffs contributed to persistent inflationary pressures, particularly in the immediate aftermath of their implementation. These inflationary pressures affected consumer spending and economic growth.
- Changes in US manufacturing competitiveness: The tariffs aimed to boost US manufacturing competitiveness, but the effects have been mixed. While some reshoring has occurred, it has not been as widespread as initially anticipated.
- Reshoring and near-shoring trends: The tariffs accelerated the trend of companies relocating manufacturing operations closer to home. However, this shift has been gradual and faces significant challenges in terms of cost and infrastructure.
- Impact on specific industries: Specific industries, such as soybeans and textiles, experienced significant disruptions due to the tariffs. The agricultural sector, for example, felt the impact of retaliatory tariffs imposed by China.
Geopolitical Implications and the US-China Relationship
Trump's 30% tariffs on China have significantly impacted the US-China relationship and broader geopolitical dynamics. The trade war has exacerbated existing tensions and created new challenges.
- Increased trade tensions: The tariffs dramatically increased trade tensions between the US and China, creating a climate of uncertainty and distrust. This impacted other aspects of bilateral relations.
- Impact on global supply chains: The disruptions to global supply chains caused by the tariffs highlighted the risks of over-reliance on a single sourcing country. This spurred efforts to diversify supply chains.
- Shifting geopolitical alliances: The trade war forced other countries to take sides or navigate carefully between the two economic superpowers, leading to a shifting geopolitical landscape.
- The role of international trade organizations: The trade war challenged the authority and effectiveness of international trade organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), prompting discussions about the need for reform.
Predicting the Landscape in Late 2025 and Beyond
Predicting the future of US-China trade relations is inherently challenging. However, several scenarios are plausible regarding the lasting legacy of the 30% tariffs.
- Potential for further tariff adjustments: Further tariff adjustments are possible, depending on the evolving political and economic climate. Negotiations and trade agreements may lead to gradual tariff reductions or targeted adjustments.
- Continued economic restructuring in both countries: Both the US and China are likely to continue restructuring their economies, adapting to the changes brought about by the trade war. This includes ongoing efforts in reshoring and nearshoring.
- Long-term impacts on global trade patterns: The long-term impacts on global trade patterns will likely include greater diversification of supply chains and a greater focus on regional trade agreements.
- Forecasting future trade relations: The future of US-China trade relations remains uncertain, dependent on factors such as geopolitical events, technological advancements, and the domestic policies of both countries.
Conclusion
This article has analyzed the multifaceted impact of Trump's 30% tariffs on China, examining their initial shockwaves, the subsequent adjustments under the Biden administration, and the long-term economic and geopolitical consequences. The legacy of these tariffs will continue to shape the US-China relationship and global trade for years to come. The ripple effects are still being felt and will continue to influence economic and geopolitical strategies for years to come.
Call to Action: Understanding the complex ramifications of Trump's 30% tariffs on China is crucial for navigating the evolving global economic landscape. Stay informed on this critical issue by continuing to research the effects of Trump's 30% tariffs on China and their impact on your industry. The impact of these tariffs is far-reaching and continues to evolve, making ongoing awareness essential.

Featured Posts
-
 48 20 000 Ultraviolette Tesseract
May 17, 2025
48 20 000 Ultraviolette Tesseract
May 17, 2025 -
 Shkembimi I Te Burgosurve Midis Rusise Dhe Ukraines Roli Kyc I Emirateve Te Bashkuara Arabe
May 17, 2025
Shkembimi I Te Burgosurve Midis Rusise Dhe Ukraines Roli Kyc I Emirateve Te Bashkuara Arabe
May 17, 2025 -
 Cybersecurity Expert Outwits Deepfake Detector Cnn Business Report
May 17, 2025
Cybersecurity Expert Outwits Deepfake Detector Cnn Business Report
May 17, 2025 -
 Japans Economic Performance Q1 2018 Impact Of Anticipated Tariffs
May 17, 2025
Japans Economic Performance Q1 2018 Impact Of Anticipated Tariffs
May 17, 2025 -
 Tuerkiye Subat 2024 Uluslararasi Yatirimlarin Durumu Ve Analizi
May 17, 2025
Tuerkiye Subat 2024 Uluslararasi Yatirimlarin Durumu Ve Analizi
May 17, 2025
