Understanding Femicide: A Look At The Statistics And Contributing Factors

Table of Contents
H2: Shocking Statistics on Femicide
H3: Global Prevalence
The global prevalence of femicide is alarming. While precise figures are difficult to obtain due to underreporting and inconsistent data collection methods across countries, available statistics paint a grim picture. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that a significant percentage of female homicides are categorized as femicide, representing a substantial portion of all violent deaths among women.
- Data from UN Women: [Insert specific data and cite the source]. This data highlights [key insights from the data].
- Data from WHO: [Insert specific data and cite the source]. This figure underscores [key insights from the data].
- Underreporting: A significant challenge in accurately assessing the global prevalence of femicide is the widespread underreporting of cases. Many incidents go unreported due to fear of retaliation, lack of trust in law enforcement, or societal stigma surrounding gender-based violence. This significantly skews the actual numbers.
H3: Regional Variations
Femicide rates vary considerably across different regions of the world, reflecting complex interplay of cultural norms, economic disparities, and legal frameworks.
- High-Prevalence Regions: [List specific regions with high rates and briefly explain potential contributing factors, e.g., weak rule of law, high rates of intimate partner violence]. Cite sources.
- Low-Prevalence Regions: [List specific regions with lower rates and briefly discuss possible explanations, e.g., strong legal protections, robust social support systems]. Cite sources.
- Visualizing Data: A map visualizing regional variations in femicide rates would provide a powerful visual representation of this global problem. (Include a map if possible).
H3: Victim Profiles
While femicide victims come from diverse backgrounds, certain patterns emerge. Understanding victim profiles helps identify vulnerable populations and tailor prevention strategies effectively.
- Age: [Insert data on the age groups most commonly affected].
- Relationship to Perpetrator: [Insert data on the relationship between victim and perpetrator – intimate partner, family member, acquaintance, stranger]. The majority of femicides are committed by intimate partners or family members.
- Socioeconomic Status: [Discuss any correlation between socioeconomic status and risk of femicide].
H2: Contributing Factors to Femicide
H3: Societal Norms and Gender Inequality
Deeply ingrained societal norms and pervasive gender inequality are fundamental drivers of femicide.
- Patriarchal Structures: In many societies, patriarchal structures grant men greater power and control over women, normalizing violence and reinforcing harmful gender stereotypes.
- Gender Stereotypes: Harmful gender stereotypes that portray women as submissive and men as dominant contribute to a culture that tolerates and even justifies violence against women.
- Harmful Masculinity: The notion of "toxic masculinity" often promotes aggression and the belief that men have a right to control women.
H3: Intimate Partner Violence (IPV)
Intimate partner violence (IPV) is a significant precursor to femicide. The escalation of IPV often follows a predictable pattern that can end tragically.
- Stages of Escalation: [Detail the stages of escalation, from verbal abuse to physical violence to ultimately, homicide].
- Early Intervention: Early intervention and support for victims of IPV are critical to preventing femicide. This includes providing safe shelters, counseling, and legal assistance.
H3: Access to Resources and Justice
Limited access to resources and justice systems significantly exacerbates the problem of femicide.
- Lack of Resources: Many women lack access to essential resources such as shelters, legal aid, and support networks, leaving them vulnerable to violence.
- Justice System Failures: Ineffective law enforcement, biased judicial systems, and inadequate protection measures contribute to impunity for perpetrators.
H3: The Role of Weapons Availability
Easy access to weapons, particularly firearms, is a critical factor that increases the risk of femicide.
- Gun Control: Stricter gun control measures can play a significant role in reducing femicide rates.
- Weapon Types: [Insert data if available on the types of weapons most frequently used in femicide].
H2: Combating Femicide: Prevention and Intervention Strategies
H3: Education and Awareness Campaigns
Education is a cornerstone of prevention. Comprehensive campaigns can challenge harmful norms and promote gender equality.
- School Programs: Integrating gender equality education into school curricula is crucial to fostering respect and challenging gender stereotypes from a young age.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Public awareness campaigns can raise awareness about femicide, its causes, and available support services.
H3: Strengthening Legal Frameworks
Stronger legal frameworks are essential to hold perpetrators accountable.
- Stricter Penalties: Implementing stricter penalties for femicide sends a clear message that such violence will not be tolerated.
- Improved Victim Protection Orders: Effective victim protection orders are critical in preventing further violence and ensuring the safety of survivors.
H3: Support Services for Survivors
Providing comprehensive support services is vital for survivors of violence.
- Shelters: Safe shelters provide temporary refuge for women escaping violence.
- Counseling: Counseling services can help survivors process trauma and rebuild their lives.
- Legal Aid: Access to legal aid ensures that survivors receive the support they need to navigate the justice system.
H3: Multi-Sectoral Collaboration
Addressing femicide requires a collaborative approach involving governments, NGOs, and communities.
- Inter-agency Collaboration: Effective coordination between different agencies is critical for a multi-pronged approach.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in prevention efforts fosters collective responsibility and ownership.
3. Conclusion
Femicide is a global crisis demanding immediate and comprehensive action. The staggering statistics, coupled with the identified contributing factors, paint a clear picture of the urgent need for transformative change. We must strengthen legal frameworks, improve access to resources and justice, and promote gender equality through widespread education and awareness campaigns. Learn more about femicide prevention and support organizations fighting femicide. Take action to end femicide. Become an advocate against femicide. Only through collective action can we hope to eradicate this horrific crime and build a world free from violence against women.

Featured Posts
-
 Klopp Real Madrid In Teknik Direktoerue Olabilir Mi
May 21, 2025
Klopp Real Madrid In Teknik Direktoerue Olabilir Mi
May 21, 2025 -
 Le Festival Le Bouillon Engagement Et Spectacles A Clisson
May 21, 2025
Le Festival Le Bouillon Engagement Et Spectacles A Clisson
May 21, 2025 -
 Saskatchewan Politics And The Curious Case Of Costco
May 21, 2025
Saskatchewan Politics And The Curious Case Of Costco
May 21, 2025 -
 Confirmation John Lithgow And Jimmy Smits In Dexter Resurrection
May 21, 2025
Confirmation John Lithgow And Jimmy Smits In Dexter Resurrection
May 21, 2025 -
 Wtt Press Conference A Revolutionary Approach To Competition
May 21, 2025
Wtt Press Conference A Revolutionary Approach To Competition
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 When Will It Rain Precise Timing And Chances Of Precipitation
May 21, 2025
When Will It Rain Precise Timing And Chances Of Precipitation
May 21, 2025 -
 Checking For Rain Get The Latest Timing And Forecast Updates
May 21, 2025
Checking For Rain Get The Latest Timing And Forecast Updates
May 21, 2025 -
 Current Rain Predictions Accurate Timing Of On And Off Showers
May 21, 2025
Current Rain Predictions Accurate Timing Of On And Off Showers
May 21, 2025 -
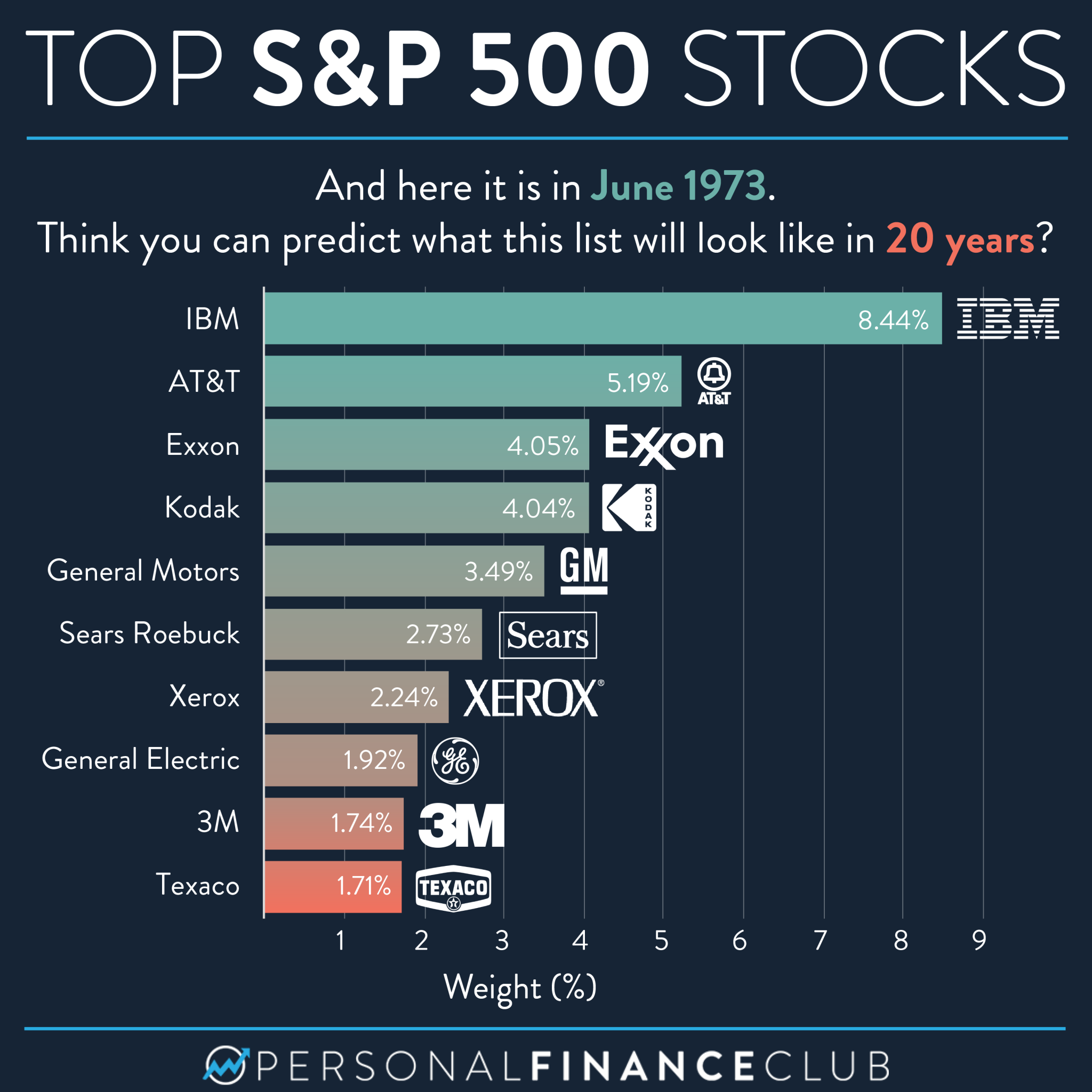 Reddits 12 Hottest Ai Stocks Should You Invest
May 21, 2025
Reddits 12 Hottest Ai Stocks Should You Invest
May 21, 2025 -
 Big Bear Ai Stock Risks And Rewards For Investors
May 21, 2025
Big Bear Ai Stock Risks And Rewards For Investors
May 21, 2025
