Understanding The Link Between Federal Debt And Mortgage Rates
Table of Contents
How Increased Federal Debt Influences Interest Rates
The relationship between government borrowing and interest rates is fundamental to understanding the impact of federal debt on mortgage rates. When the government needs to borrow money to finance its spending – exceeding tax revenue – it issues Treasury bonds. This increased borrowing increases the overall demand for loanable funds within the economy. The bond market, a crucial part of this process, sees a rise in demand for these bonds, pushing their prices up and consequently, driving down their yields (the return an investor receives). However, this increased demand for loanable funds doesn't just affect government bonds.
- Increased government borrowing increases demand for loanable funds. This heightened demand extends beyond government securities.
- Higher demand pushes interest rates upward across the board. This isn't limited to government bonds; it affects interest rates on various financial instruments.
- This includes rates on government bonds, corporate bonds, and mortgages. The ripple effect is felt throughout the financial system.
- The Federal Reserve's role in managing interest rates and inflation. The Federal Reserve (the Fed) plays a crucial role in managing this process, aiming to balance economic growth with inflation control. Actions like quantitative easing (injecting money into the economy) or raising interest rates (making borrowing more expensive) significantly influence the relationship between federal debt and interest rates.
The Federal Reserve's actions, such as quantitative easing or interest rate hikes, directly influence the overall cost of borrowing. For instance, raising interest rates makes borrowing more expensive, potentially slowing down inflation but also increasing the cost of mortgages.
The Direct Impact on Mortgage Rates
The general increase in interest rates, influenced by factors such as increased federal debt, directly translates to higher mortgage rates. Mortgage pricing isn't solely determined by the lender; it's intricately linked to the broader economic climate, including the level of federal debt.
- Mortgage rates are intrinsically linked to the overall yield curve. The yield curve represents the relationship between short-term and long-term interest rates.
- Rising yields on Treasury bonds often lead to higher mortgage rates. As the government borrows more, yields on Treasury bonds tend to rise, affecting the cost of borrowing for mortgages.
- Mortgage lenders factor in the increased risk associated with higher interest rate environments. Lenders adjust their rates to reflect the perceived risk of lending in a higher interest rate environment.
- The impact on affordability and demand for housing. Higher mortgage rates directly impact the affordability of homes, potentially reducing demand and slowing down the housing market.
Different mortgage types are affected differently. Fixed-rate mortgages lock in a specific interest rate for the loan's term, providing certainty but leaving borrowers vulnerable to rising rates if they refinance later. Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) offer initially lower rates but adjust periodically based on market conditions, making them more volatile in high-debt environments. Historical data clearly shows a correlation between increases in federal debt and subsequent rises in mortgage rates. For example, [insert relevant data or statistic here showing the correlation].
Indirect Effects of Federal Debt on the Housing Market
The consequences of high federal debt on the housing market extend beyond the direct impact on mortgage rates. Indirect effects include:
- High inflation erodes purchasing power, impacting home affordability. When the government borrows heavily, it can lead to inflation, diminishing the value of money and making homes less affordable.
- Economic uncertainty can reduce consumer confidence and dampen housing demand. High levels of federal debt often create economic uncertainty, making potential homebuyers hesitant to commit to large purchases.
- Investor behavior can be influenced by economic forecasts related to federal debt. Investors may become cautious in a high-debt environment, potentially impacting housing market investment and development.
- Potential impact on government-sponsored housing programs. Government programs aimed at supporting homeownership may face budget constraints under high levels of federal debt.
Historical periods, such as [insert example of historical period], illustrate how high federal debt has correlated with significant fluctuations in the housing market, often leading to periods of instability.
Strategies for Navigating High Mortgage Rates in a High-Debt Environment
Even in a high-debt environment with elevated mortgage rates, there are strategies to navigate the housing market successfully:
- Improve credit score to qualify for better rates. A higher credit score often translates to lower interest rates.
- Consider different mortgage types and terms. Exploring options like 15-year mortgages (higher monthly payments but lower overall interest) or ARMs (depending on your risk tolerance) can be beneficial.
- Explore options like down payment assistance programs. Government and non-profit programs may provide assistance with down payments, making homeownership more accessible.
- Monitor economic indicators and interest rate forecasts. Staying informed about economic trends and forecasts can help you make more informed decisions.
- Seek professional financial advice. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance tailored to your financial situation.
Careful budgeting, saving diligently for a down payment, and fully understanding the long-term financial implications of mortgage debt are crucial aspects of responsible homeownership, regardless of prevailing economic conditions.
Conclusion
The relationship between federal debt and mortgage rates is complex but undeniable. Increased federal debt often leads to higher interest rates, directly impacting mortgage rates and indirectly influencing the broader housing market through factors such as inflation and economic uncertainty. Understanding this connection is crucial for making informed decisions about your personal finances and real estate investments. By staying informed about economic indicators and government policies, you can better navigate the complexities of the housing market and make smart choices regarding your homeownership journey. Understanding the relationship between federal debt and mortgage rates is crucial for smart financial planning. Stay informed and make informed choices about your homeownership journey.

Featured Posts
-
 Major Drone Attack On Ukraine Russias Latest Assault
May 19, 2025
Major Drone Attack On Ukraine Russias Latest Assault
May 19, 2025 -
 Will A Canadian Tire Hudsons Bay Partnership Succeed A Detailed Analysis
May 19, 2025
Will A Canadian Tire Hudsons Bay Partnership Succeed A Detailed Analysis
May 19, 2025 -
 Impact Of New Regulations On Londons Vibrant Live Music Scene
May 19, 2025
Impact Of New Regulations On Londons Vibrant Live Music Scene
May 19, 2025 -
 Fa Cup Final 2024 Haalands Wembley Struggle Persists
May 19, 2025
Fa Cup Final 2024 Haalands Wembley Struggle Persists
May 19, 2025 -
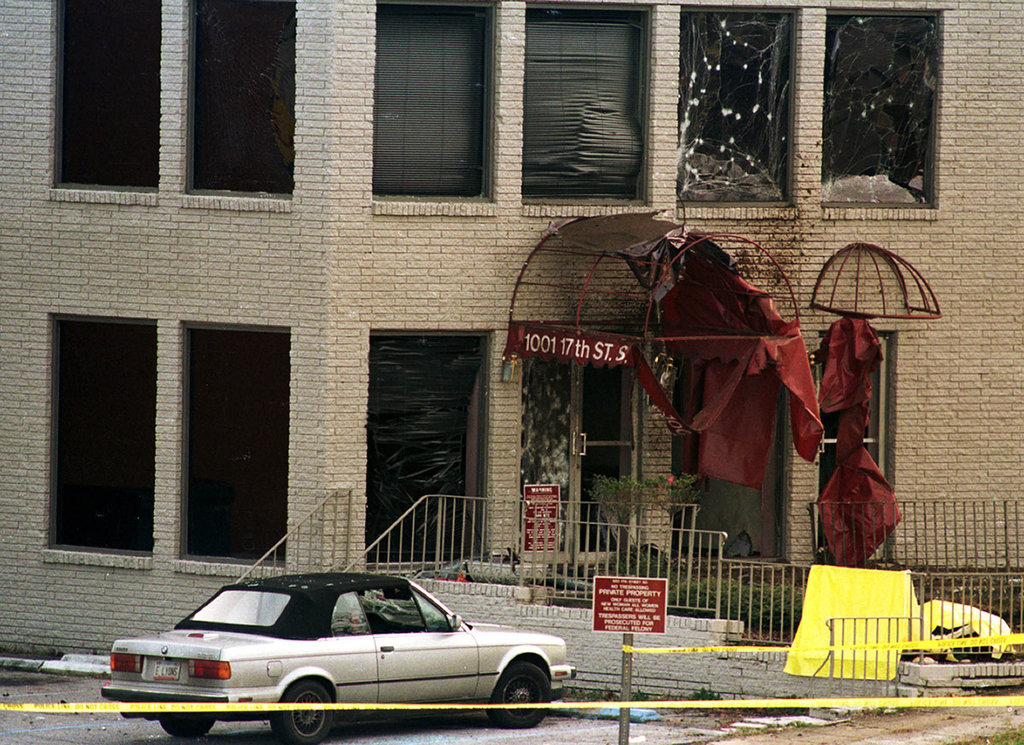 Fbi Confirms Likely Death Of California Fertility Clinic Bombing Suspect
May 19, 2025
Fbi Confirms Likely Death Of California Fertility Clinic Bombing Suspect
May 19, 2025
