Amsterdam Stock Market Crash: 7% Plunge Amidst Trade War Fears

Table of Contents
The Amsterdam stock market suffered a seismic shock, plummeting 7% in a single day. This dramatic fall, a significant event for investors and the Dutch economy, was primarily triggered by escalating trade war fears and the resulting global economic uncertainty. This article delves into the causes, consequences, and potential future implications of this Amsterdam stock market crash, examining its impact on Dutch businesses and the government's response. We will explore keywords such as "Amsterdam stock market crash," "trade war," "market volatility," and "economic uncertainty" to provide a comprehensive analysis.
Causes of the Amsterdam Stock Market Crash
The sharp decline in the Amsterdam stock market is directly linked to the growing anxieties surrounding global trade wars and their potential impact on the Dutch economy. Investor confidence, a crucial driver of market stability, crumbled under the weight of these escalating tensions.
Global Trade Tensions
The ongoing US-China trade war, along with other international trade disputes, significantly impacted global markets. The Netherlands, with its export-oriented economy, is particularly vulnerable to these disruptions.
- Rising tariffs and trade barriers: Increased tariffs imposed by various countries led to higher prices for imported goods and decreased competitiveness for Dutch exporters.
- Uncertainty in global supply chains: Trade disputes created uncertainty and disruptions in global supply chains, impacting businesses reliant on timely delivery of goods and materials.
- Reduced investor confidence in international trade: The unpredictable nature of trade policies eroded investor confidence, leading to a flight from riskier assets, including stocks.
Impact on Dutch Businesses
Several sectors within the Netherlands felt the brunt of the trade war anxieties.
- Decreased export demand: Dutch businesses, particularly those heavily reliant on exports, faced reduced demand from international markets due to trade restrictions and economic slowdowns in key trading partners.
- Increased input costs: Tariffs and trade barriers increased the cost of imported raw materials and intermediate goods, squeezing profit margins for many businesses.
- Potential for job losses: Reduced demand and higher costs led to concerns about potential job losses within affected industries, further dampening investor confidence.
Impact of the 7% Plunge on the Amsterdam Stock Market
The 7% plunge had immediate and significant consequences for the Amsterdam stock market, primarily reflected in the AEX index, the benchmark index for the Euronext Amsterdam exchange.
Investor Sentiment and Volatility
The crash triggered a significant shift in investor sentiment, characterized by increased market volatility.
- Sharp decline in trading volume: Investors became hesitant, reducing trading activity as uncertainty gripped the market.
- Increased market uncertainty: The sudden and sharp drop amplified existing anxieties, creating a climate of uncertainty and speculation.
- Flight to safety: Investors moved their capital into safer assets, such as government bonds, reducing the demand for stocks and further driving down prices.
Economic Implications for the Netherlands
The crash's broader economic consequences extend beyond the stock market, impacting various aspects of the Dutch economy.
- Potential slowdown in economic growth: The reduced investor confidence and decreased business activity threaten to slow down the Netherlands' economic growth.
- Increased unemployment: Job losses in export-oriented sectors and reduced overall economic activity could lead to higher unemployment rates.
- Reduced consumer spending: Economic uncertainty and fears of job losses can lead to decreased consumer confidence and reduced spending, further dampening economic activity.
Government Response and Mitigation Strategies
The Dutch government responded to the crisis by implementing various measures to stabilize the market and support affected businesses.
Fiscal and Monetary Policies
The government and the Dutch central bank deployed a range of fiscal and monetary policies to stimulate economic activity.
- Government spending initiatives: Increased government spending on infrastructure projects and other stimulus programs aimed at boosting demand.
- Tax cuts or incentives for businesses: Tax relief and incentives aimed at encouraging business investment and job creation.
- Central bank interventions: The central bank may have lowered interest rates to make borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers, stimulating investment and spending.
Support for Affected Businesses
The government also introduced specific programs to support businesses severely impacted by the market crash.
- Loan guarantees or subsidies: Government-backed loans and subsidies to help businesses stay afloat and avoid layoffs.
- Job retention schemes: Programs to support businesses in retaining employees during difficult times.
- Financial assistance programs: Direct financial aid provided to businesses in particularly hard-hit sectors.
Future Outlook and Predictions for the Amsterdam Stock Market
The future outlook for the Amsterdam stock market depends heavily on the resolution of global trade tensions and the overall health of the global economy.
Trade War Resolution
A resolution to the trade disputes could significantly impact market recovery.
- Increased investor confidence: A de-escalation of trade tensions would likely boost investor confidence, leading to increased investment and market stability.
- Market stabilization: Reduced uncertainty would contribute to market stabilization and a potential rebound in stock prices.
- Economic growth rebound: Improved trade relations could lead to a resurgence in economic growth, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Long-Term Economic Impacts
The crash's long-term effects on the Dutch economy and its global competitiveness remain to be seen.
- Structural changes in the economy: The crisis could trigger structural changes within the Dutch economy, potentially leading to greater diversification and reduced reliance on specific export markets.
- Shifts in global trade patterns: The trade disputes could reshape global trade patterns, requiring Dutch businesses to adapt to new market realities.
- Increased economic resilience: The crisis may lead to increased resilience within the Dutch economy, enabling it to better withstand future shocks.
Conclusion
The 7% plunge in the Amsterdam stock market, driven by escalating trade war fears, represents a significant economic event with wide-ranging consequences for the Netherlands. The crash exposed the vulnerability of export-oriented economies to global trade disputes and highlighted the importance of government intervention to mitigate economic shocks. Understanding market volatility and its potential impact is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. To make informed investment decisions, monitor the Amsterdam stock market closely, understand the impact of trade wars on global markets, and develop strategies to mitigate risk in volatile markets. Stay informed about economic news and market trends through reputable financial news sources to navigate the complexities of investing during periods of uncertainty. Learning about economic indicators and different investment strategies will allow you to approach the Amsterdam stock market and other markets with greater confidence.

Featured Posts
-
 Eurovision 2025 Concert Conchita Wurst And Jj In The Village
May 24, 2025
Eurovision 2025 Concert Conchita Wurst And Jj In The Village
May 24, 2025 -
 Annie Kilner Shows Off Huge Diamond Ring After Walker Sighting
May 24, 2025
Annie Kilner Shows Off Huge Diamond Ring After Walker Sighting
May 24, 2025 -
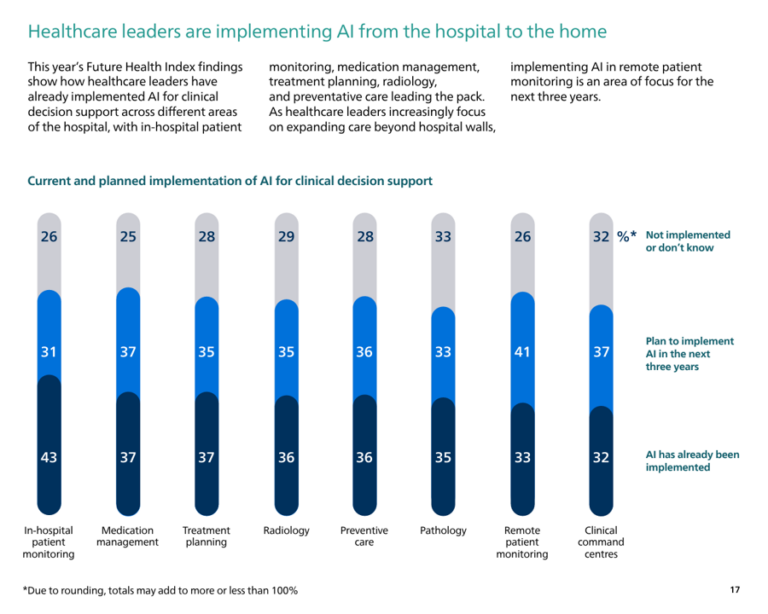 Philips Future Health Index 2025 Urgent Call To Action On Ai In Healthcare
May 24, 2025
Philips Future Health Index 2025 Urgent Call To Action On Ai In Healthcare
May 24, 2025 -
 Frankfurt Equities Opening Dax Continues Record Breaking Ascent
May 24, 2025
Frankfurt Equities Opening Dax Continues Record Breaking Ascent
May 24, 2025 -
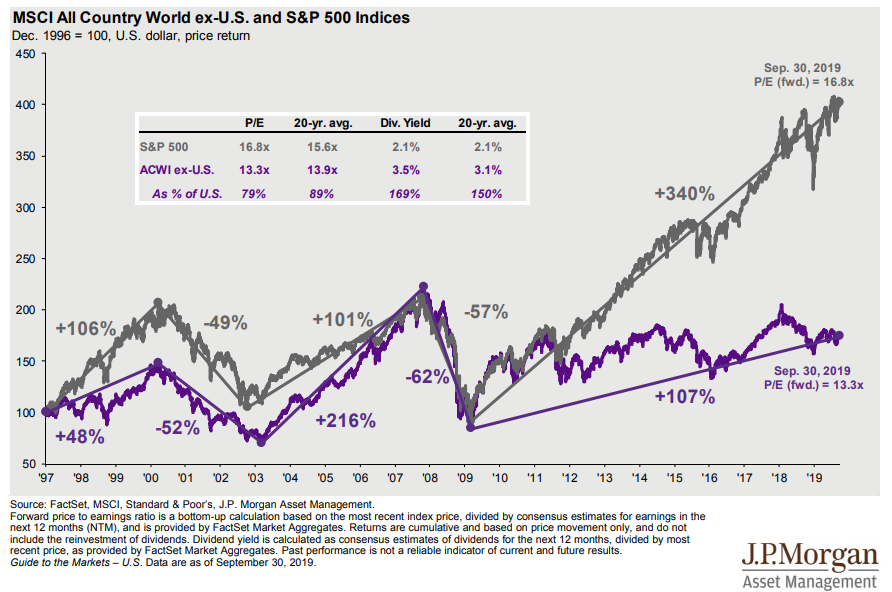 Amundi Msci World Ex Us Ucits Etf Acc A Deep Dive Into Net Asset Value
May 24, 2025
Amundi Msci World Ex Us Ucits Etf Acc A Deep Dive Into Net Asset Value
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
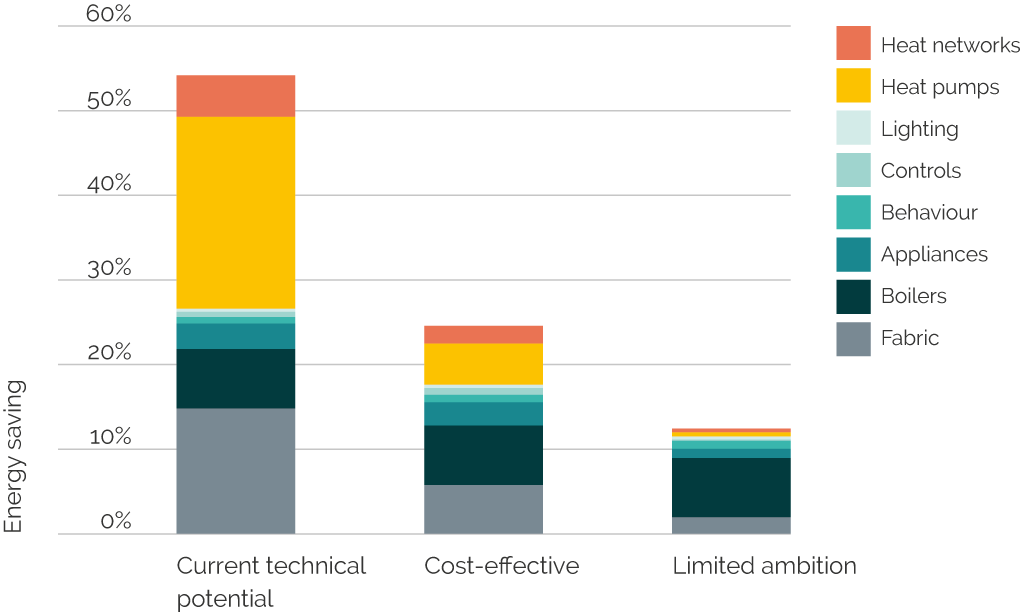 Impact Of Sses 3 Billion Spending Reduction On Energy Sector And Consumers
May 24, 2025
Impact Of Sses 3 Billion Spending Reduction On Energy Sector And Consumers
May 24, 2025 -
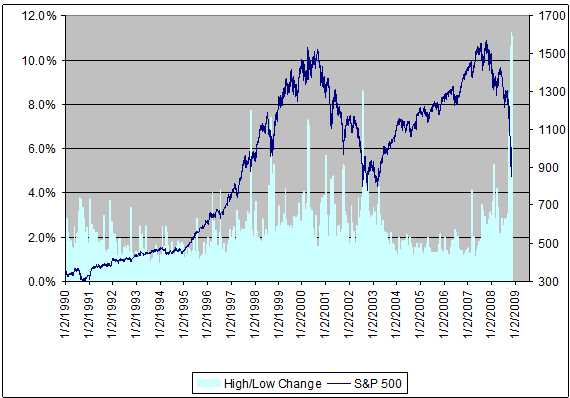 Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations Bof As Insight For Investors
May 24, 2025
Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations Bof As Insight For Investors
May 24, 2025 -
 Investigating Thames Water The Issue Of Executive Bonuses
May 24, 2025
Investigating Thames Water The Issue Of Executive Bonuses
May 24, 2025 -
 Thames Water Understanding The Debate Surrounding Executive Pay
May 24, 2025
Thames Water Understanding The Debate Surrounding Executive Pay
May 24, 2025 -
 Analysis Of Sses 3 Billion Spending Cut And Its Long Term Effects
May 24, 2025
Analysis Of Sses 3 Billion Spending Cut And Its Long Term Effects
May 24, 2025
