Jerome Powell: How Tariffs Could Hinder The Fed's Mandate

Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures from Tariffs
Tariffs exert significant inflationary pressure on the US economy, directly challenging the Fed's mandate of price stability.
Increased Prices for Consumers
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers. This inflationary effect forces the Fed to consider countermeasures, potentially impacting economic growth and employment.
- Example: Increased tariffs on steel and aluminum have rippled through the manufacturing sector, leading to higher prices for automobiles and other manufactured goods. This increased cost of production is often passed directly to consumers.
- Example: Tariffs on consumer goods like clothing and electronics directly translate to higher prices at the retail level, reducing consumer purchasing power and potentially dampening consumer confidence. This reduction in consumer spending can further impact economic growth.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Beyond direct price increases, tariffs create significant disruptions in global supply chains. This unpredictability makes accurate economic forecasting incredibly difficult for the Fed.
- Impact: Businesses face increased uncertainty, leading to decreased investment in expansion and hiring, further slowing economic growth.
- Impact: Consumers face higher prices and potentially limited choices as supply chains are disrupted and certain goods become scarcer. This scarcity can also lead to increased prices on substitute goods.
Impact on Employment and Economic Growth
The uncertainty and increased costs associated with tariffs significantly impact employment and overall economic growth, directly contradicting the Fed's mandate of maximum employment.
Reduced Business Investment
The uncertainty surrounding tariffs discourages businesses from investing in expansion, hiring, and research and development. This directly impacts job creation and overall economic growth.
- Factor: Businesses postpone or cancel expansion plans due to the fear of further tariff increases and unpredictable trade policies.
- Factor: Increased costs associated with tariffs reduce profit margins, making investments less attractive and reducing the incentive for businesses to expand.
Retaliatory Tariffs and Global Trade Wars
Tariffs often provoke retaliatory measures from other countries, escalating into trade wars that damage global economic growth and negatively affect the US economy. The Fed must navigate these complex geopolitical factors while maintaining its mandate.
- Consequence: Reduced US exports harm American businesses and employment in export-oriented sectors.
- Consequence: Increased uncertainty undermines business confidence, further reducing investment and hindering economic growth.
Challenges for Monetary Policy
The inflationary pressures and economic uncertainties created by tariffs present significant challenges for the Fed's monetary policy.
Difficulty in Targeting Inflation
The inflationary pressures created by tariffs make it harder for the Fed to maintain its inflation targets. The Fed might need to raise interest rates, potentially slowing economic growth and negatively impacting employment.
- Dilemma: Raising interest rates too aggressively risks causing a recession, increasing unemployment and potentially further harming economic growth.
- Dilemma: Raising interest rates too slowly risks allowing inflation to spiral out of control, eroding consumer purchasing power and potentially leading to greater economic instability.
Limited Policy Tools
Tariffs are a fiscal policy issue, outside the direct control of the Fed's monetary policy tools. This limits the Fed's ability to effectively address the economic challenges created by tariffs.
- Limitation: Monetary policy tools are primarily focused on interest rates and money supply. The Fed's impact on fiscal policy decisions relating to tariffs is indirect and limited.
- Limitation: The Fed has limited influence over government trade policy, meaning that it must react to the consequences of tariff decisions rather than directly influencing them.
Conclusion
The impact of tariffs on the US economy presents a significant challenge for Jerome Powell and the Federal Reserve. Tariffs fuel inflation, disrupt supply chains, hinder business investment, and complicate the already difficult task of achieving both maximum employment and price stability. The Fed's ability to fulfill its mandate is directly hampered by the unpredictable and often counterproductive effects of tariffs. Understanding the complex relationship between tariffs and the Fed's mandate is crucial for navigating the current economic landscape. To stay informed on the ongoing economic effects of tariffs and their impact on the Federal Reserve's actions, continue to follow expert analysis on the interplay between tariffs and the Fed, and the broader implications for monetary policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Over January 6th Coverage
May 26, 2025
Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Over January 6th Coverage
May 26, 2025 -
 The Turning Point George Russells Solution To Mercedes Performance Issue
May 26, 2025
The Turning Point George Russells Solution To Mercedes Performance Issue
May 26, 2025 -
 Wrongful Glasgow Airport Arrest Feature Film In The Works
May 26, 2025
Wrongful Glasgow Airport Arrest Feature Film In The Works
May 26, 2025 -
 Extreme V Mware Price Increase At And T Details 1 050 Jump Proposed By Broadcom
May 26, 2025
Extreme V Mware Price Increase At And T Details 1 050 Jump Proposed By Broadcom
May 26, 2025 -
 Planning Your Visit To Dr Terrors House Of Horrors
May 26, 2025
Planning Your Visit To Dr Terrors House Of Horrors
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
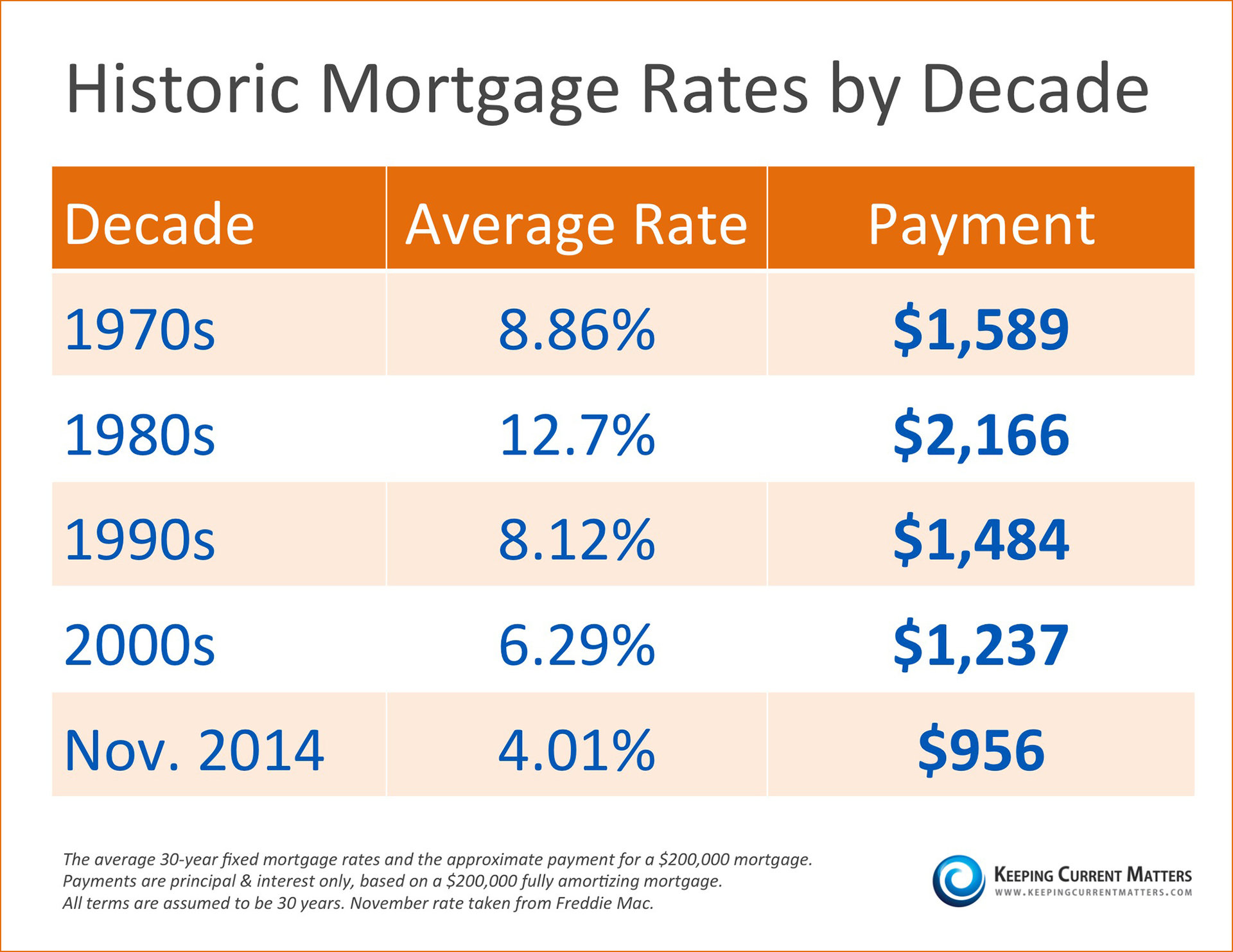 Personal Loan Interest Rates Your Guide To Finding The Best Deal Today
May 28, 2025
Personal Loan Interest Rates Your Guide To Finding The Best Deal Today
May 28, 2025 -
 Check Todays Personal Loan Interest Rates And Apply Now
May 28, 2025
Check Todays Personal Loan Interest Rates And Apply Now
May 28, 2025 -
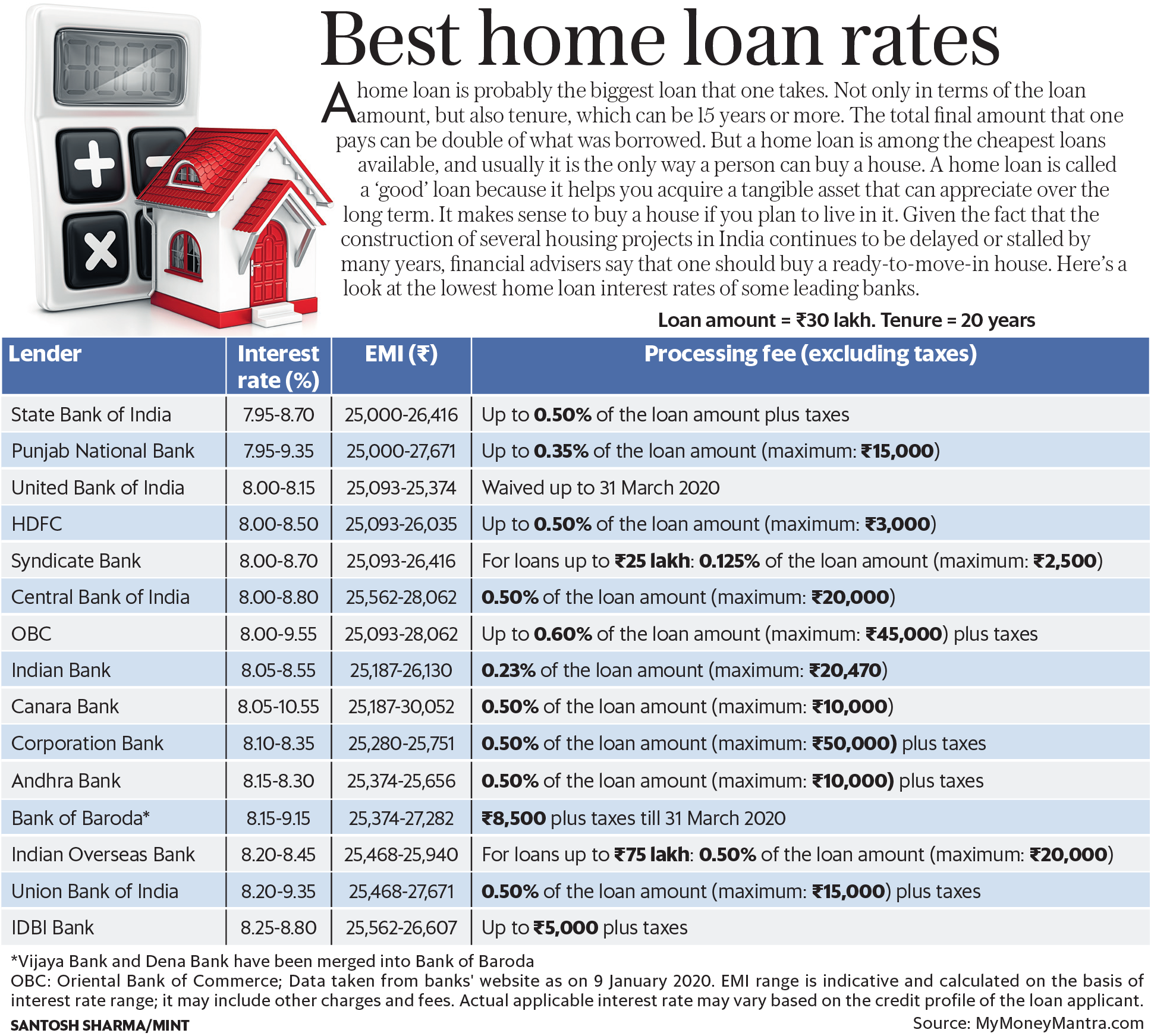 Personal Loan Interest Rates Today How To Get The Lowest Rate
May 28, 2025
Personal Loan Interest Rates Today How To Get The Lowest Rate
May 28, 2025 -
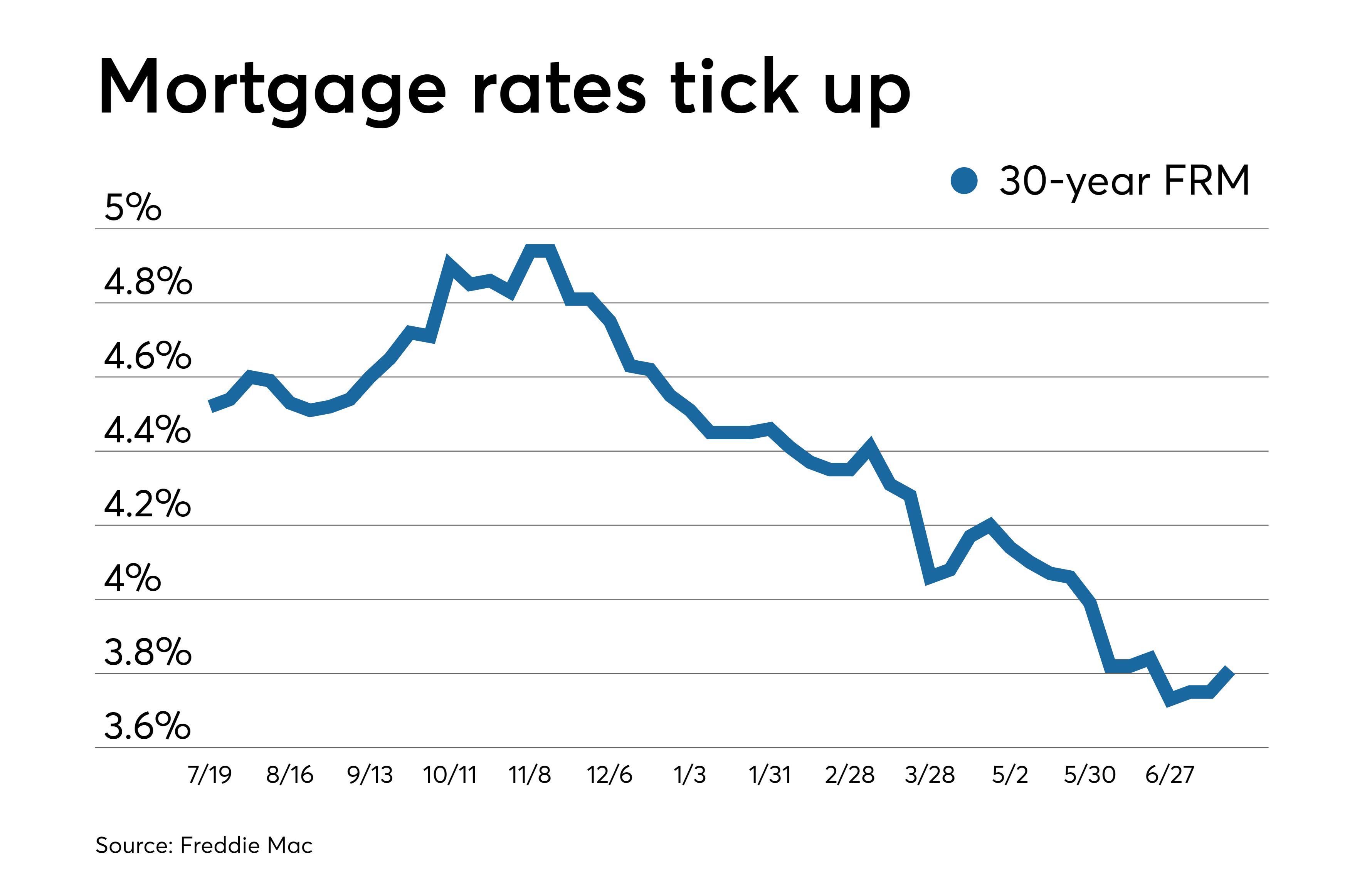 Find The Perfect Personal Loan Todays Best Interest Rates
May 28, 2025
Find The Perfect Personal Loan Todays Best Interest Rates
May 28, 2025 -
 6000
May 28, 2025
6000
May 28, 2025
