Trump's Trade War: A 10% Tariff Baseline And The Path To Exceptions
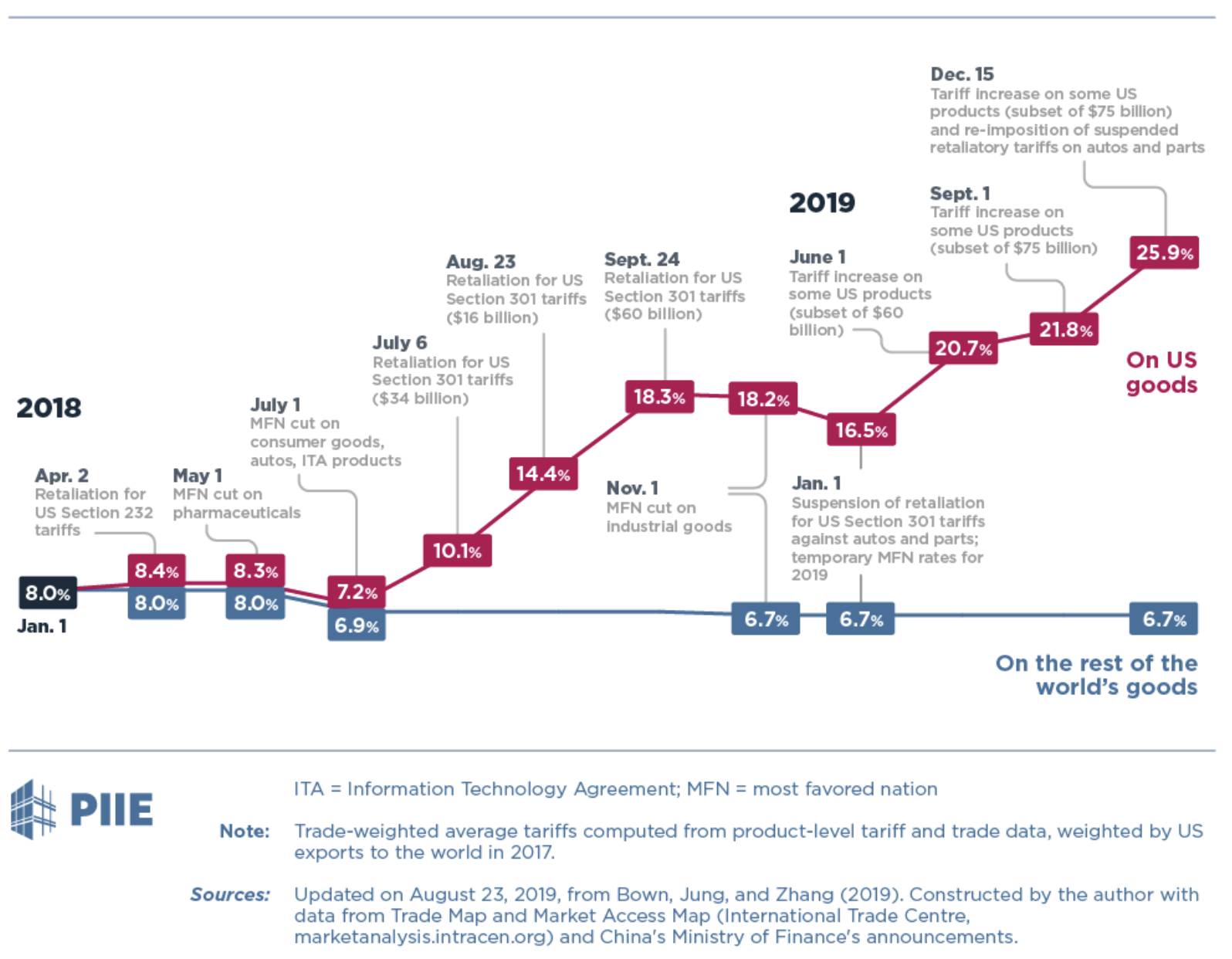
Table of Contents
Understanding the 10% Tariff Baseline
Initial Implementation and Targeted Goods
The 10% tariff, a key element of Trump's trade war, initially targeted a vast array of goods imported from various countries, primarily China. The rationale behind this move was to protect American industries from what the administration viewed as unfair trade practices and to encourage domestic production. However, the broad scope of the tariffs led to unforeseen consequences.
-
Affected Industries and Products: The tariffs impacted numerous sectors, including:
- Steel and aluminum
- Consumer electronics
- Agricultural products (soybeans, for example)
- Machinery and equipment
- Textiles and apparel
-
Economic Impact: The 10% tariff immediately resulted in increased prices for consumers, reduced competitiveness for some US businesses relying on imported components, and significant disruption to global supply chains. Studies from various economic institutions revealed varying estimates of job losses and overall economic impact, highlighting the complexity of measuring the full effects.
Economic Consequences of the 10% Tariff
The ripple effects of the 10% tariff were far-reaching and complex. Inflation rose, impacting consumer purchasing power, and some businesses experienced job losses due to decreased demand and increased input costs. Global supply chains were significantly disrupted as companies scrambled to find alternative sourcing options.
- Inflation and Consumer Prices: The tariffs contributed to increased prices for a range of consumer goods, impacting household budgets and overall economic growth.
- Job Losses and Business Closures: While the administration's intention was to create jobs domestically, some businesses faced closures or significant job losses due to reduced competitiveness.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Companies were forced to adjust their supply chains, often incurring higher costs and lead times due to sourcing from alternative locations.
The Process of Obtaining Tariff Exceptions
The complexity of Trump's trade policy wasn't limited to the tariffs themselves; the process of obtaining exceptions proved equally challenging for many businesses.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Procedures
Businesses seeking relief from the 10% tariff needed to demonstrate significant economic hardship and prove that no domestic alternatives existed. This required extensive documentation, detailed financial statements, and a thorough explanation of the potential negative impact of the tariffs.
- Application Process: The application process was rigorous and time-consuming. Businesses needed to submit detailed applications to the relevant government agencies, often navigating bureaucratic hurdles and lengthy waiting periods.
- Challenges and Hurdles: The high burden of proof, complex regulations, and limited transparency in the decision-making process presented significant challenges for businesses seeking exceptions.
Factors Considered in Exception Approval
The government considered various factors when evaluating applications for tariff exceptions, including:
- National Security: Applications that demonstrated a critical impact on national security were often prioritized.
- Economic Impact: The potential economic consequences of the tariffs on the applicant and the broader economy played a significant role.
- Availability of Domestic Alternatives: The availability of comparable products within the US was a crucial factor in determining eligibility.
Successful applicants demonstrated compelling evidence addressing all these factors. Conversely, unsuccessful applications often lacked sufficient substantiation or failed to meet the strict eligibility criteria.
Appealing Denied Exceptions
Businesses whose applications for tariff exceptions were denied could appeal the decision through established channels, though the success rate was often low.
- Appeal Process: The appeal process involved further documentation and arguments, often requiring legal expertise and significant resources.
- Likelihood of Success: The appeal process was lengthy and complex, with limited success rates. Specific resources and guidance were often scarce.
Long-Term Impacts and Lessons Learned from Trump’s Trade War
Trump's trade war left lasting scars on the global trade landscape, influencing international relations and forcing businesses to adapt to new realities.
Shifts in Global Trade Relationships
The trade war significantly strained relationships between the US and key trading partners, particularly China. This led to a broader rise in protectionist sentiment globally, prompting other nations to implement their own trade barriers.
- Changes in Trade Agreements: The trade war exposed vulnerabilities in existing trade agreements and prompted discussions about their reform or replacement.
- Increased Protectionist Sentiment: The trade war fueled a global rise in protectionism, with countries adopting more restrictive trade policies.
Strategies for Businesses to Mitigate Future Trade Risks
The experience of Trump's trade war offers invaluable lessons for businesses seeking to navigate future trade uncertainties.
- Diversify Supply Chains: Reducing reliance on single-source suppliers can mitigate the impact of future trade disruptions.
- Hedge Against Currency Fluctuations: Employing hedging strategies can protect businesses from adverse currency movements related to trade policies.
- Engage in Lobbying Efforts: Participating in lobbying efforts to influence trade policy can provide businesses a stronger voice in shaping future trade regulations.
- Stay Informed: Staying abreast of trade policy developments is critical to proactive risk management.
Conclusion: Trump’s Trade War: Understanding the 10% Tariff and its Legacy
Trump's 10% tariff, a defining element of his trade war, proved to be a complex and far-reaching policy with lasting consequences. Understanding the 10% tariff baseline, the difficulties of obtaining exceptions, and the long-term impacts is crucial for navigating the complexities of trade policy. Businesses must learn from this period, adapting their strategies to mitigate future trade risks. To further master tariff exceptions and understand the impact of the 10% tariff, explore resources from the U.S. government and other reputable economic research institutions. By understanding the past, businesses can better prepare for the future of international trade.

Featured Posts
-
 Xi Jinpings Security Czar Leads Exclusive China U S Trade Talks
May 10, 2025
Xi Jinpings Security Czar Leads Exclusive China U S Trade Talks
May 10, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Net Worth Drops Teslas Challenges And Market Volatility
May 10, 2025
Elon Musks Net Worth Drops Teslas Challenges And Market Volatility
May 10, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Impact Of The 2025 Nhl Trade Deadline On The Playoffs
May 10, 2025
Analyzing The Impact Of The 2025 Nhl Trade Deadline On The Playoffs
May 10, 2025 -
 Sensex Gains 200 Points Nifty Surges Past 22 600 Market Update
May 10, 2025
Sensex Gains 200 Points Nifty Surges Past 22 600 Market Update
May 10, 2025 -
 Nottingham Attack Investigation Experienced Judge Takes The Lead
May 10, 2025
Nottingham Attack Investigation Experienced Judge Takes The Lead
May 10, 2025
